Introduction to Multi-Agent Systems
In the evolving landscape of Generative AI, Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) are emerging as a game-changing approach for automation, decision-making, and AI-driven collaboration. Unlike traditional single-agent models, MAS involves multiple autonomous AI agents, each equipped with a defined role, working together to solve complex tasks with higher efficiency, reduced biases, and improved accuracy.
This blog is part of an ongoing series exploring multi-agent architecture, highlighting leading frameworks such as AutoGen, CrewAI, and more. These tools empower developers to build sophisticated AI-driven bots capable of seamless collaboration and dynamic problem-solving.
Understanding Multi-Agent Systems in AI
A Multi-Agent System (MAS) is an advanced AI framework where multiple AI-powered agents interact and collaborate to achieve defined objectives. Each agent possesses a specific persona, role, and contextual understanding, allowing them to contribute unique perspectives to the problem-solving process.
How Multi-Agent Systems Differ from Single-Agent Models
- Single-Agent Systems: A centralized AI makes all decisions, limiting the scope of innovation and adaptability.
- Multi-Agent Systems: Multiple intelligent agents engage in real-time discussions, analyze various possibilities, and deliver superior results by integrating diverse viewpoints.
For example, in software development, one agent may generate application code, while another reviews, refines, and optimizes it. Through iterative feedback loops, these agents enhance output quality, reduce hallucinations, and eliminate biases, ultimately producing higher-quality AI-generated results.
Key Benefits of Multi-Agent Architectures
1. Task Specialization & Separation of Concerns
- Each agent is assigned specific responsibilities, optimizing efficiency and improving outcomes.
- Multi-agent structures integrate fine-tuned language models and toolsets for superior task execution.
2. Scalability & Modularity
- AI-driven agents break down complex challenges into manageable units, enhancing problem-solving capabilities.
- Agents can be modified or improved independently without affecting the entire system.
3. Diversity in Decision-Making
- By incorporating different perspectives, multi-agent setups reduce AI biases and hallucinations, leading to more accurate outputs.
4. Reusability & Adaptability
- Once created, agents can be repurposed for various applications, fostering an ecosystem of AI-driven problem solvers.
- With the right orchestration framework (AutoGen, CrewAI, etc.), agents can work seamlessly on diverse, complex tasks.
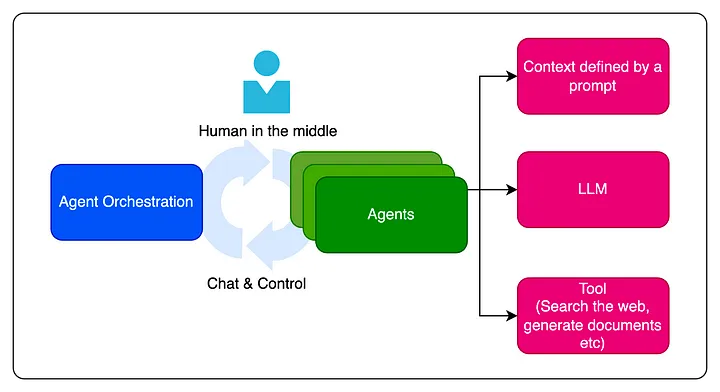
Core Components of Multi-Agent AI Systems
- Intelligent Agents: AI-driven bots with predefined roles, responsibilities, and behaviors.
- Communication & Connections: Defines how agents interact and exchange information.
- Orchestration Mechanism: Determines agent workflow (e.g., sequential, hierarchical, or bi-directional collaboration).
- Human-In-The-Loop (HITL): Many applications require human oversight for decision-making and validation.
- Tool Integration: Agents use specialized tools for data retrieval, web searches, document analysis, and coding tasks.
- Language Model (LLM) Backbone: AI agents are powered by large language models (LLMs) to enable reasoning, inference, and content generation.
Leading Multi-Agent Frameworks in 2025
With multi-agent architectures gaining traction, several frameworks have emerged to simplify development and deployment. Let’s explore the most prominent ones:
1. OpenAI Assistant
Best For: Long-term AI collaboration & multimodal interactions.
- Supports persistent multi-agent interactions for extended use cases.
- Equipped with a code interpreter, file management tools, and seamless agent-to-agent communication.
2. AutoGen (Microsoft)
Best For: Orchestration-driven multi-agent AI development.
- Open-source framework designed for modular AI agent creation.
- Features AutoGen Studio, an intuitive no-code development platform for AI-driven automation.
3. CrewAI
Best For: Role-based AI agents for collaborative workflows.
- Facilitates autonomous AI agents with specialized roles.
- Optimized for team-based AI operations, enabling AI collaboration for complex problem-solving.
4. LangGraph (Built on LangChain)
Best For: Stateful multi-agent coordination.
- Enables cyclic workflows, inspired by Apache Beam & Pregel.
- Ideal for multi-step AI processes requiring long-term memory & context tracking.
5. Dragonscale’s Multi-Agent System
Best For: Enterprise-level AI automation.
- Adapts dynamically to real-world business problems, optimizing operational workflows.
- AI agents are designed to handle high-complexity decision-making.
The Future of Multi-Agent AI: What’s Next?
As AI-driven automation advances, multi-agent frameworks will play a pivotal role in transforming industries, including:
- Software Engineering: AI-powered teams handling end-to-end development & debugging.
- Customer Support: Multi-agent AI responding to queries, analyzing feedback, and optimizing interactions.
- Healthcare AI: Medical agents assisting in diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient support.
References & Further Reading
- AutoGen (Microsoft)
- CrewAI Documentation
- LangGraph on LangChain
- Dragonscale AI Systems
- OpenAI Assistant API
🚀 Stay ahead of the AI revolution! Follow us for more in-depth insights on Multi-Agent AI, Generative AI, and Future AI Technologies—Follow us on LinkedIn
